Gemini News Archive
Dusty Old Star Offers Window to Our Future, Astronomers Report
Press Release | 2005 September 8
Astronomers have glimpsed dusty debris around an essentially dead star where gravity and radiation should have long ago removed any sign of dust. The discovery might provide insights into our own solar system’s eventual demise several billion years from now.
A Chinese Dragon and a Knotted Galactic Embrace
Press Release | 2005 August 26
The Gemini Observatory released a pair of images today that capture the dynamics of two very different interactions in space.
Gemini Uncovers 'Lost City' of Stars
Press Release | 2005 August 10
Astronomers using the 8-meter Gemini South telescope have revealed that the galaxy NGC 300 has a large, faint extended disk made of ancient stars, enlarging the known diameter of the galaxy by a factor of two or more.
Gemini Observatory Shows That "10th Planet" Has a Pluto-Like Surface
Press Release | 2005 July 29
Gemini Observatory has obtained a preliminary spectrum of 2003 UB313, the so-called "10th planet".
Dustiest Star Could Harbor a Young Earth
Press Release | 2005 July 20
A relatively young star located about 300 light-years away is greatly improving our understanding of the formation of Earth-like planets.
Gemini Prepares for Planet Searching with NICI
Web Feature | 2005 July 7
Gemini Observatory is actively looking for sub-stellar mass companions using the existing Adaptive Optics (AO) system Altair on Gemini North, and building the specialized near-infrared coronagraph (NICI) with its own AO system for Gemini South.
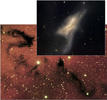
Amateur Astronomers Travel Deep Into Stellar Cocoon Using Gemini
Press Release | 2005 May 17
Recently a Canadian amateur astronomy group took advantage of a rare opportunity and used the Gemini 8-meter telescope to look more deeply into the remains of a particular stellar nursery than anyone ever has.
Background Information: Laser Guide Stars
Press Release | 2005 April 28
An Laser Guide Star is produced by a relatively low power laser beam that shines up from a telescope into a layer of sodium gas in our upper atmosphere, creating a temporary artificial "star."
Dusting for Clues: Gemini Discovers Evidence for Colliding Bodies in Planet Forming Disk
Press Release | 2005 January 13
Astronomers using T-ReCS have observed new details in the dusty disk surrounding the nearby star Beta Pictoris which show that a large collision between planetary-sized bodies may have occurred there as recently as the past few decades.
Stunning Images Herald Opening of Gemini Observatory's Image Gallery
Press Release | 2005 January 10
A pair of beautiful images (NGC 1532/NGC1531 and NGC 2467) released today in San Diego at the 205th meeting of the American Astronomical Society marks the formal debut of the Gemini Observatory’s Image Gallery.
Gemini Observatory Welcomes 2005 with Release of Galactic Fireworks Image
Press Release | 2005 January 1
In the image, the face-on spiral galaxy NGC 6946 is ablaze with colorful galactic fireworks fueled by the births and deaths of multitudes of brilliant, massive stars.
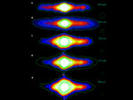
New Clouds Add to Titan's Mystery
Press Release | 2004 December 15
A U.S. team has discovered a new phenomenon in the atmosphere of Saturn’s largest moon Titan. The new images reveal atmospheric disturbances at Titan’s temperate mid latitudes—about halfway between the equator and the poles.
Gemini Observatory Announces Selection of 2005 StarTeachers
Press Release | 2004 December 9
Gemini Observatory announced the six teachers selected for the 2005 StarTeachers exchange program between Hawaii and Chile.
Why do Galaxies in the Young Universe Appear so Mature?
Press Release | 2004 October 8
Gemini Deep Deep Survey (GDDS) revealed that the galaxies appear to be more fully formed and mature than expected at the early stage in the evolution of the Universe.
Mystery Object Neither Star Nor Brown Dwarf
Press Release | 2004 October 5
Astronomers using the Gemini North and Keck II telescopes have peered inside a violent binary star system to find that one of the interacting stars has lost so much mass to its partner that it has regressed to a strange, inert body resembling no known star type.
Gemini South is First 8-10 Meter Class Telescope With Protected Silver Coatings
Press Release | 2004 June 9
The Gemini South 8-meter telescope gets a new coating of silver, increasing the sensitivity of the mid-infrared instruments on the telescope.
Cosmic Powerhouses Dwell In Humble Galactic Homes
Press Release | 2004 May 25
Celestial Beacon Sheds New Light on Stellar Nursery
Press Release | 2004 March 30
A timely discovery by American amateur astronomer Jay McNeil, followed immediately by observations at the Gemini Observatory, has provided a rare glimpse into the slow, yet violent birth of a star about 1,500 light-years away.
Massive Old Star Reveals Secrets On Deathbed
Press Release | 2004 January 26
Astronomers have obtained the most detailed observations ever of an old but otherwise normal massive star just before and after its life ended in a spectacular supernova explosion.
Looking Sharp: Images from New Gemini Spectrograph Rival View from Space
Press Release | 2003 June 30
Among the images and spectra acquired during recent commissioning of the Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) on the Gemini South Telescope, one image is particularly compelling - the Hickson Compact Group 87 (HCG87).