
Capability Summary
- Total wavelength range = 360−1030 nm
Imaging (Read more)
- 5.5’ square field of view
- 0.0807"/pixel spatial sampling
- broad and narrow band filters
Spectroscopy
- Resolutions (See grating options)
- 1260−8800 for 0.25" slit (depending on grating)
- 210−1460 for 1.5" slit (depending on grating)
- Modes
Guiding Options
- GMOS On-Instrument Wavefront Sensor (OIWFS)
- Periferal Wavefront Sensor 2 (PWFS2)
Get the sensitivity
Get to the integration time calculator
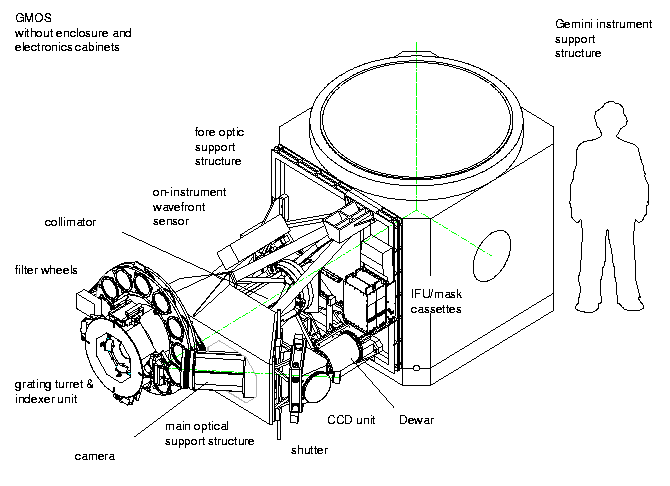
The GMOS were built by a collaboration of the Astronomy Technology Centre at the ROE, the University of Durham in the UK and the Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in Canada. GMOS-N was delivered in July 2001 with GMOS-S following in December 2002.
Announcements
Instrument Team
gn Instrument Scientist

gn Additional Support Staff
- Kristin Chiboucas
- Teo Močnik
- Hyewon Suh
- Jennifer Andrews
- Brian C. Lemaux
- Clara Martínez-Vázquez
- Emanuele Farina
- Jennifer Miller
- Sunny Stewart
Email: GMOS_N_science@gemini.edu
gs Instrument Scientist
