
 |
Definition of an Astronomical Source in the ITC |
Definition of an astronomical source involves specification of the spatial profile, the brightness normalisation and the spectrum.
The astronomical target may be a point or an extended source.
The nominal point source has a size defined by the image quality constraint and air mass (selected as part of the observing conditions), the wavelength (selected by the colour filter or dispersive element as part of the instrument properties) and the wavefront sensor (selected as part of the telescope properties). The adopted extent of the point source (in arcsec) is reported in the ITC results.
Several different extended sources are (to be) available. Currently a 2-dimensional Gaussian profile with user-defined FWHM (in arcsec) and an extended source with uniform surface brightness may be selected. The user-defined FWHM is defined as the image size delivered in the telescope focal plane (i.e. it should include seeing). An arbitary spatial profile imported from an external file will be available at a later date.
The source flux density or, for uniform extended sources, surface brightness are specified in familiar astronomical units available via the pull-down menus. The source brightness is converted into the ITC internal units of photons/s/nm/m^2 (optionally, per square arcsec) using the relationships described below. The source brightness can be specified at a wavelength that is not the observing wavelength provided that the chosen (redshifted) spectrum extends across the entire wavelength range of interest (e.g. that defined by the colour filter).
Zeropoints giving continuum photons/s/nm/m^2 for a zero magnitude source are assumed to be:
| Waveband | Wavelength (um) | Zeropoint (photons/s/nm/m^2) |
| U | 0.36 | 7.59 * 10^7 |
| B | 0.44 | 1.46 * 10^8 |
| V | 0.55 | 9.71 * 10^7 |
| R | 0.67 | 6.46 * 10^7 |
| I | 0.87 | 3.90 * 10^7 |
| J | 1.25 | 1.97 * 10^7 |
| H | 1.65 | 9.6 * 10^6 |
| K | 2.20 | 4.5 * 10^6 |
| L' | 3.76 | 9.9 * 10^5 |
| M' | 4.77 | 5.1 * 10^5 |
| N | 10.5 | 5.1 * 10^4 |
| Q | 20.1 | 7.7 * 10^3 |
These values were derived from the CIT system used in the STScI units conversin tool (UBVRI) and Cohen et al. (1992. AJ, 104, 1650; JHKL'M' from Vega and Sirius for 10 and 20um).
The photon flux density (in photons/s/nm/m^2) as a function of the source brightness in AB magnitudes is given by:
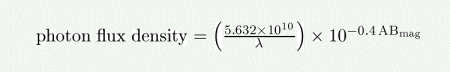
where lambda is the wavelength in nm. This is equivalent to the formal definition in Oke & Gunn (1983. ApJ, 266, 713).
The photon flux density (in photons/s/nm/m^2) as a function of the source brightness in Jy (i.e. 10^-26 W/m^2/Hz) is given by:
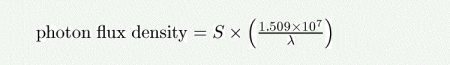
where lambda is the wavelength in nm.
The photon flux density (in photons/s/nm/m^2) as a function of the source brightness in W/m^2/um is given by:
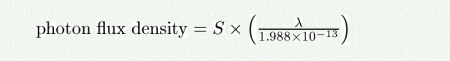
where lambda is the wavelength in nm.
The photon flux density (in photons/s/nm/m^2) as a function of the source brightness in ergs/s/cm^2/Angstrom is given by:
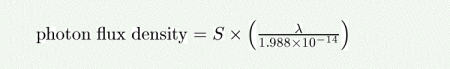
where lambda is the wavelength in nm.
The photon flux density (in photons/s/nm/m^2) as a function of the source brightness in ergs/s/cm^2/Hz is given by:
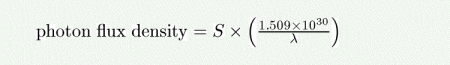
where lambda is the wavelength in nm.
The source spectrum is selected from the available libraries of stellar and non-stellar spectra, model emission line + continuum, and black body, power law and user-defined spectra. Different options are availale depending on the instrument in question. The spectrum may be redshifted by an arbitrary amount. If the selected (redshifted) spectrum does not completely cover the observing wavelength range, as defined by the colour filter or dispersive element, either an error is reported by the ITC or the spectrum is padded with leading or trailing zeros.
For spectroscopic calculations, the source spectrum is smoothed to the resolution of the spectrograph as given by the dispersing element with an entrance aperture defined by the slit width, or source extent if narrower (some exceptions are noted for specific instruments). Note that the stellar and non-stellar libraries may have an intrinsic resolution less than that of the instrument or a coarser sampling. In all cases they are re-sampled to the appropriate dispersion within the ITC.
The sky transmission and sky background spectra employed currently have a resolution of ~1nm and sampling of ~0.5nm. Hence at higher instrument spectral resolutions, the sky lines will not be treated correctly.
The Pickles (1998; PASP, 110, 863) stellar library covers optical and near-IR wavelengths out to 2.5um across a broad range of spectral types (O5 to M9) and luminosity classes (I, III and V). We have extended these spectra out to 6um, arbitrarily adopting the slope of the K0III star for all spectral types. More accurate spectrophotometry will be inserted in the ITC library as it becomes available.
Rest-frame optical and near-IR spectra:
This generates a Gaussian emission line on top of a flat (per wavelength interval) continuum. The specified line flux and continuum flux density override the brightness normalisation defined as part of the spatial profile.
User-defined source spectra can be used instead of the existing template and model SEDs. Note the following restrictions on file format:
Last update August 17, 2006; Rachel Mason
Original version by Phil Puxley, Ted von Hippel and Marianne Takamiya. Mid-IR
spectra from Kevin Volk and Tom Geballe.